What is an IT Safe Room: The Most Important Room in Critical Network Infrastructure
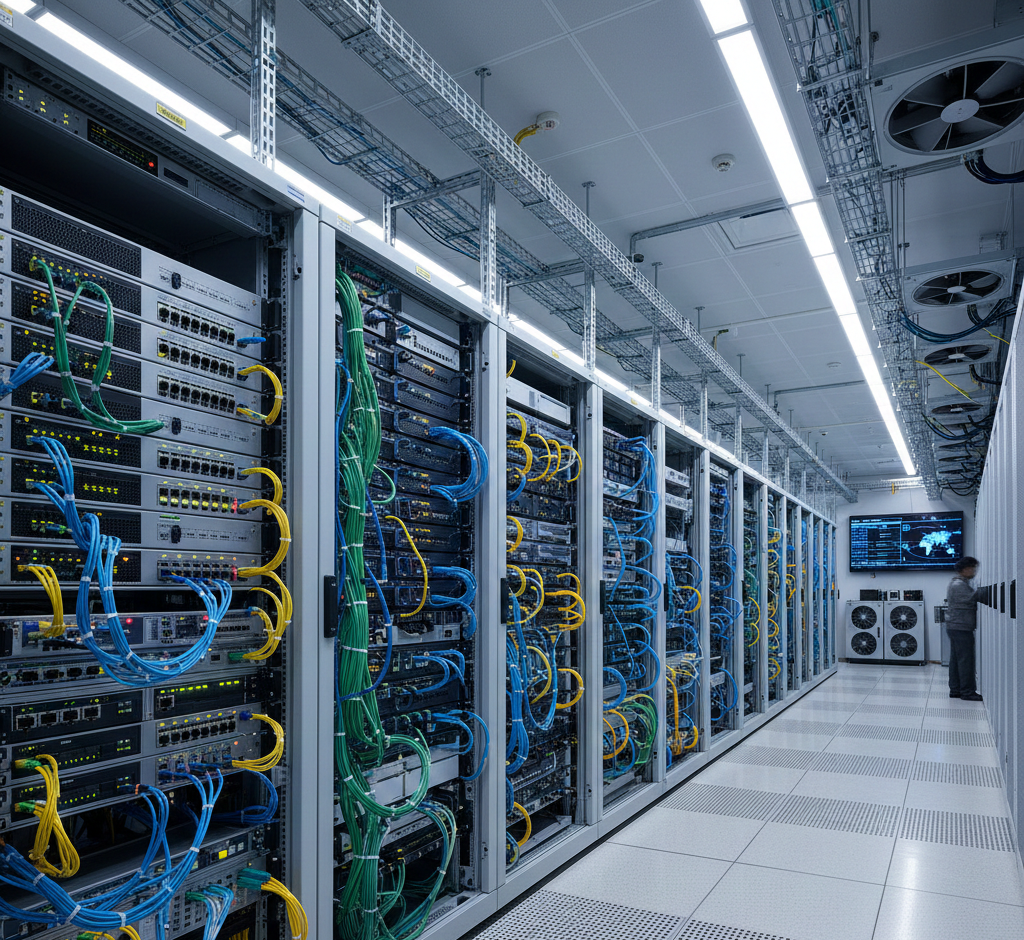
The IT Safe Room (often referred to as a Vault Room or Secure Server Room) is the most protected and strategic environment within the IT infrastructure of a company, government agency, data center, or financial institution.
It is designed to shield servers, network assets, data, and critical systems against virtually any type of threat—ranging from internal failures to extreme events such as fires, explosions, floods, or intrusion attempts.
In other words:➡ It is the last place that is allowed to fail.
1. What Exactly is an IT Safe Room?
An IT Safe Room is an armored and certified environment built to ensure maximum physical and logical security. It follows international standards, such as ABNT NBR 15247 (which defines physical resistance requirements) and ISO 27001 (Information Security Management), functioning like a “bank vault,” but designed exclusively for IT equipment.
Inside, you will find:
- Critical servers
- Storage and backup systems
- Core switches and high-capacity routers
- Firewalls
- Mission-critical equipment
- Monitoring systems
It acts as the beating heart of the network infrastructure.
2. Why is the IT Safe Room So Important?
Because it is a location designed to keep operating even when everything else goes wrong. A failure in this room could mean:
- Data loss
- Total company downtime
- Paralysis of financial systems
- Shutdown of airports, hospitals, or public agencies
- Closure of entire business operations
It is built to prevent unavailability, serving as a central part of Disaster Recovery and High Availability policies.
3. Essential Protections for an IT Safe Room
Below are the most common protections that distinguish a Safe Room from a standard server room:
a) Resistance to Extreme Fire
The structure is built with special panels capable of resisting:
- High temperatures
- Smoke
- Flames
- Combustion explosions
The goal is to prevent fire from reaching the equipment even if the building itself is burning.
b) Protection Against Water and Floods
The room must resist:
- Flooding
- Pipe bursts
- Firefighting water runoff
It is generally elevated, utilizing a raised floor (technical floor) and drainage systems.
c) Physical Shielding
The construction uses reinforced panels that protect against:
- Structural impacts
- Vandals
- Break-in attempts
- External explosions
Everything is designed to prevent physical access or damage to the servers.
d) Electrical Protection
It includes:
- Redundant UPS (Industrial Uninterruptible Power Supply)
- Generators
- Grounding and equipotential bonding
Nothing inside can power down, burn out, or be left unprotected.
e) Highly Controlled Climate
Precision air conditioning is used (not standard split units), featuring:
- Exact temperature control
- Stabilized humidity
- Redundancy (N+1 or 2N)
- Pressurization
Servers do not forgive thermal failures.
f) Rigid Access Control
Typically uses:
- Biometrics
- Two-factor authentication (2FA)
- 24-hour surveillance cameras
- Entry and exit logs
- Automatic fire doors
Access is strictly limited to authorized personnel only.
g) Fire Suppression System
The IT Safe Room must have a fire detection and containment system that uses clean agents (such as inert gases like FM-200 or Novec 1230). These extinguish fires without corroding or damaging electronic equipment.
h) 24/7 Monitoring and Alarms
Sensors for:
- Smoke
- Temperature
- Vibration
- Humidity
- Door openings
- Motion
Everything is connected to security systems.
4. Who Uses an IT Safe Room?
Any organization that cannot afford to stop—known as critical operation environments:
- Data Centers
- Banks
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
- Airports
- Hospitals
- Public Agencies
- Large Industries
- Companies with essential ERPs
They can also be found in shopping malls, corporate buildings, and university campuses.
5. IT Safe Room vs. Standard Server Room: What is the Difference?
| Feature | IT Safe Room | Standard Server Room |
| Fire Resistance | High (Certified) | Low |
| Water Protection | Certified | Almost none |
| Shielding | Reinforced/Armored | Standard structure |
| Access Control | Extreme | Medium/High |
| Climate Control | High Precision | Conventional |
| Redundancy | 100% | Partial |
| Purpose | Mission Critical | General Operation |
6. The Technician’s Role in an IT Safe Room
If you work with networks, cabling, or infrastructure, here is what you need to know when entering this environment:
- ✔ Everything must be extremely organized: Patch panels, fibers, trays, labels, and cable cuts must be perfect.
- ✔ Zero improvisation: Nothing can be “jerry-rigged,” a “quick fix,” or “left for later.”
- ✔ High standard of cleanliness: Not even dust is allowed—the environment is strictly controlled.
- ✔ Cables and fibers always identified: Cable management is essential.
- ✔ Restricted access: You will almost always enter accompanied or with specific authorization.
- ✔ Maintenance usually off-hours: Interventions are often scheduled outside business hours or during low-traffic periods because any mistake can impact critical systems.
Final Thoughts
The IT Safe Room is the most important and protected environment in the entire network infrastructure.
It exists to ensure that critical systems never stop, even in the face of disasters, electrical failures, fires, or intrusion attempts. It is a room built to keep the operation alive, at any cost.
For professionals such as cable technicians, network engineers, and infrastructure specialists, understanding this environment is fundamental for working in large corporate and high-availability settings.